Connect to Infrastructure
Objective
Retrieve credentials for connecting to the various components of your organization’s infrastructure.
User Provisioning
To access live infrastructure, you must first have an account in your organization’s identity provider (IdP). 1 This account with be used to sign in to all service providers.
If your organization’s administrators have not already provisioned your account, ask them now. You will need to follow this guide to set up your user for the first time.
Once your user is provisioned, make sure you are able to access your organization’s Authentik dashboard: 2

The applications you see will vary based on your organization’s settings.
Accessing AWS
If your organization granted you AWS access, you should see AWS in your Authentik dashboard. You can click on the app to get brought to the access portal showing your individual account access:
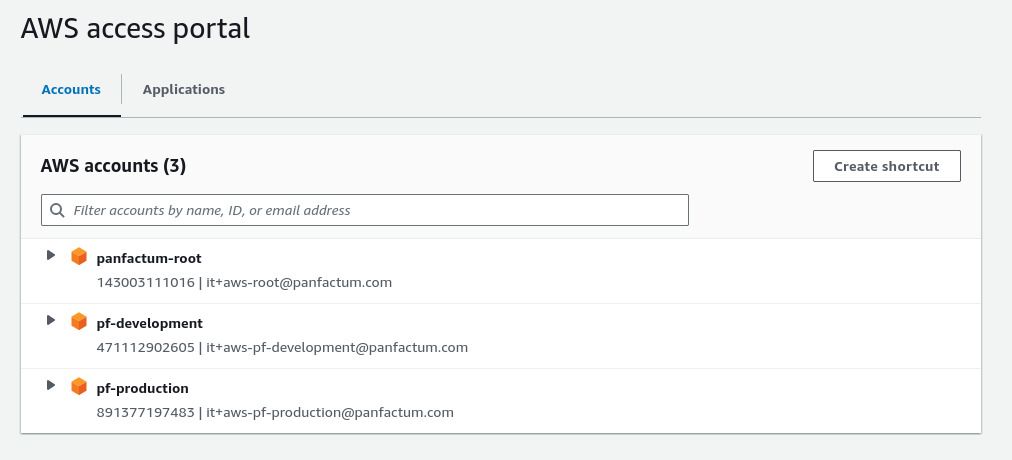
Your visible accounts and roles will vary based on your organization’s settings.
AWS CLI Access
These accounts and roles are already available for use inside your local repository. They are configured under the aws_dir directory (defaults to .aws).
Access is made available via AWS CLI/SDK profiles. You can view all your organization’s profiles by running aws configure list-profiles.
Each profile is of the format <account>-<role>.
You may not have access to all of your organization’s profiles. Check the access portal to see which accounts and roles you can use.
You can set your active profile by setting the AWS_PROFILE environment variable (e.g., export AWS_PROFILE=<your_profile>) or by passing the --profile <your_profile> flag to the aws CLI.
Let’s confirm this works:
Set
AWS_PROFILEto a profile you have access to.Run
aws sso loginto complete the single sign-on verification.Run
aws sts get-caller-identity. This should successfully return a result that looks like this:891377197483 arn:aws:sts::891377197483:assumed-role/AWSReservedSSO_Superuser_ed8b0abf4bb50ae8/jack@panfactum.com AROA47CRYUGV33VTVQCPO:jack@panfactum.com
Accessing Kubernetes
For each AWS account that you have access to, you can view the information about their deployed Kubernetes clusters via the Web UI: 3
Log into an account
Navigate to the appropriate AWS region (top right dropdown)
Navigate to the Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) page (via the search box)
Select a cluster
You should see a dashboard that looks like this:

Kubernetes CLI Access
The above dashboard is read-only. If you want to make changes to your cluster, you will need to access your clusters from the CLI. This will require setting up your kubeconfig file.
We provide an easy way to do this by performing the following actions within your organization’s repository:
Copy the
config.user.example.yamlfile in yourkube_dirfolder (defaults to.kube) toconfig.user.yaml.Update the
config.user.yamlto include the clusters you want to access and what AWS profile you want to use for that access. See the reference docs for the specific syntax.Run
pf-update-kubeto create your kubeconfig file.Select a cluster context by running
kubectx.Run
kubectl cluster-infoand you should see a successful result like the following:Kubernetes control plane is running at https://83063DDB274B2A04B6A7DC29DCB1740E.gr7.us-east-2.eks.amazonaws.com CoreDNS is running at https://83063DDB274B2A04B6A7DC29DCB1740E.gr7.us-east-2.eks.amazonaws.com/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
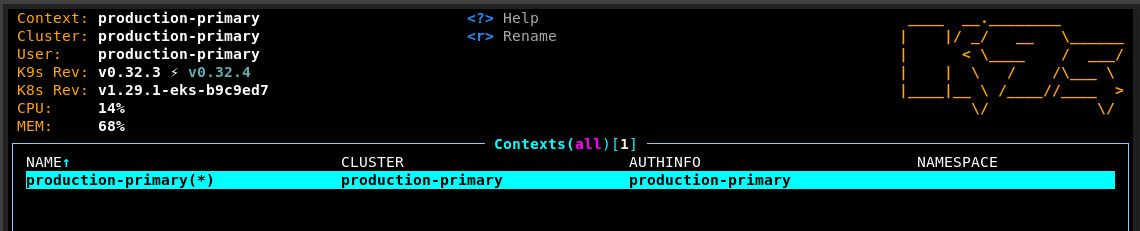
In the Panfactum stack, we highly recommend k9s as the tool for interactively interfacing with your Kubernetes clusters. We will reference it often in our documentation, so you should gain familiarity.
Launch it now via k9s:
Next Steps
🎉 You are now all set up to begin working with live infrastructure in the Panfactum stack. 🎉
Here are some ideas for next steps:
Footnotes
The IdP itself should have already been provisioned in the bootstrapping guide. ↩
If you are not sure the URL, ask an organization administrator or refer to your organization’s internal documentation. ↩
You can see what accounts and regions your clusters are deployed to by examining the
environments_dirfolder in your repository (defaults toenvironments). Search foraws_eksmodule folders. Ask an organization administrator if your need further guidance. ↩